By Owen Smith
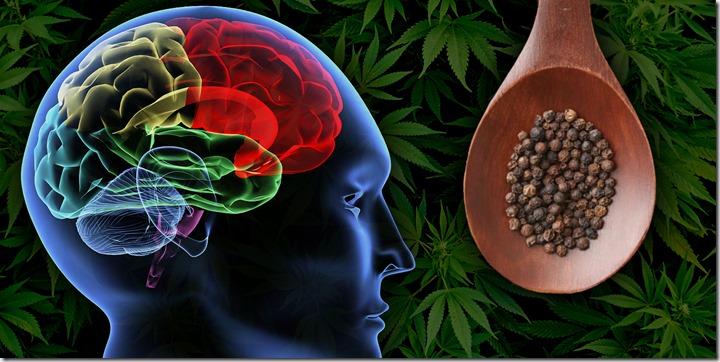
While working at the Victoria Cannabis Buyers Club I was able to teach some of the members about Black Pepper. While benefiting from the medicinal effects of THC, these patients suffered from bouts with anxiety while medicating. Most patients who have tried this simply took a few sniffs of the black pepper to receive an almost immediate effect. Others have reported that after chewing on pepper corns they felt relief within an hour, but that may be a delay most would seek to avoid. So how does this work? The Aug. 2011 British Journal of Pharmacology: Cannabinoids in Biology and Medicine, Part 1 includes numerous articles exploring the nature of the cannabis plants’ chemical dynamism. In the article “Taming THC,” scientists report having discovered more than a hundred terpenes that “may contribute meaningfully to the entourage effects of cannabis-based medicinal extracts.” Terpenes create the many scents of cannabis and are shared among the plant kingdom. Scientists explored how these aromatic oils synergize and mitigate the active cannabinoids contributing to an entourage effect.
Cannabis in known to produce a wide variety of effects from rendering a individual wide-awake to sending them into a sound sleep. Growers have been tailoring their heirloom heritage varieties of cannabis to uniformly exhibit certain cannabinoid/terpene profiles to produce particular effects. CBD is quickly becoming an essential component to combat the unwelcome effects of using THC rich cannabis, such as anxiety. Another option may be to introduce terpenes from other plant sources to mitigate the effects.
Ed Rosenthal, author of many books on cannabis, relates that the myrcene in mangos can increase the quality of low potency cannabis when eaten one hour before medicating. Anecdotal evidence suggests that the terpene alpha-pinene is alerting, limonene is “sunshine-y,” and beta-myrcene is sedating. As the names suggest, pinene is abundant in pine needles and limonene in lemons. Traditional responses to cannabis induced anxiety include pinene-rich black pepper, limonene-rich citrus, and calamus root high in myrcene. Myrcene is also found in hops (Humulus), the only other member of the Cannabaceae plant family. “Cannabis terpenoids and flavonoids may also increase cerebral blood flow, enhance cortical activity, kill respiratory pathogens, and provide anti-inflammatory activity.”(source)
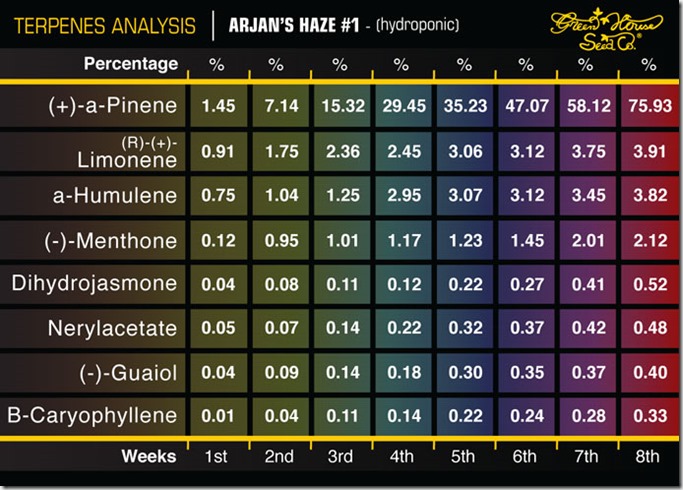
(image: GreenHouse Seeds)
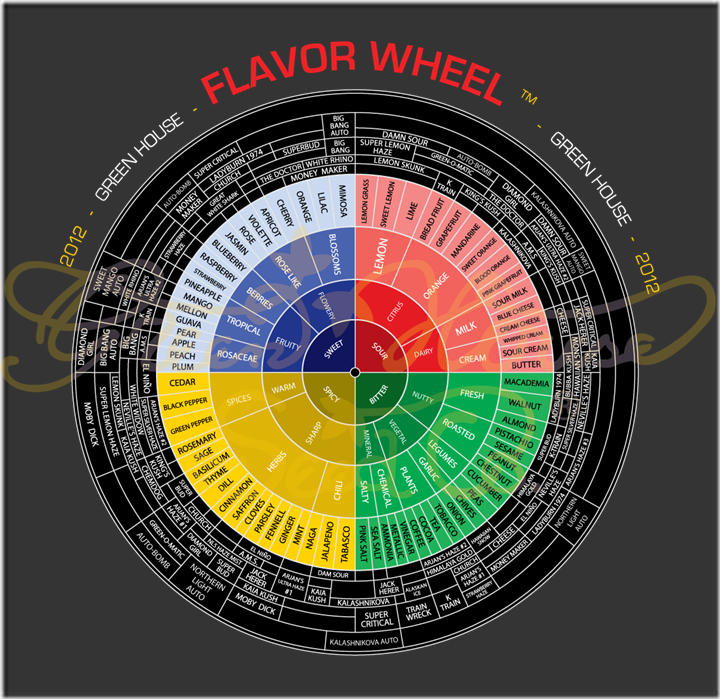
Scientists have discovered that beta-caryophyllene (BCP), which is another terpene that contributes to the aroma and flavour, also found in other herbs, spices, and food plants, activates the CB2 receptor and acts as a non-psychoactive anti-inflammatory. Because it binds to a cannabinoid receptor […] and since it is an FDA approved food additive and ingested daily with food, it is the first known dietary cannabinoid.(source) Leading the way on terpene identification is Green House Seed Company in Holland who have performed spectral analysis of each of their strains and developed a flavour wheel identifying 16 different terpenes to help individuals decide on their strain of choice.
(image: GreenHouse Seeds)
Cannabis Science Inc. is exploring the possibility that certain terpenes act as building blocks for the production of cannabinoids, with the hope that this will open up to cultivators the opportunity to manipulate cannabinoids to desired ratios. they are exploring how terpenes act synergistically with other terpenes to either catalyze or inhibit the formation of other compounds within a plant.
Up until now, drug companies have been focusing on single synthetic compounds that can be patented and brought to market. In light of these discoveries, scientists isolating cannabinoids into synthetic compounds have to consider the terpene interaction as another variable potentially responsible for the plants therapeutic effects. Cannabis grown with care and attention to the curing process will contain more terpenes. Many terpenes are FDA approved and therefore easy to obtain for testing.